MLPS Assessment
Abstract:
The new Multi-Level Protection Scheme (MLPS)2.0 standard has been released since 2019 and now it takes place more and more from the government entities into the enterprises. This article is the instruction of get MLPS assessment or how to get companies as conform as possible to the MLPS standard for mainly enterprises.

Due to the development of the nationalsecurity stand, and the cybercrimes occur more and more frequently in China, toprotect the Chinese economy and for Chinese people’s livelihoods, China released the cyber-security law (Cybersecurity Law of the People’s Republic of China, i.e. CSL) in June, 2017. In article 21 of the CSL, that all the network operators shall fulfill the MLPS.
The MLPS is a normative document to help network operators to grade their information system/network and help maintain and protect it.
The MLPS was already drafted and practiced since2008. It was firstly to be considered dedicated for government entities to protect the national network security. But after 2017, as stated in CSL, all the network operators (incl. Key industrial companies, or even WFOE) should be obligated to follow the standard of MLPS to protect the network they operate.
1.1.Legal Reference
- Cybersecurity Law of the People’s Republic of China
- Regulations of the People’s Republic of China for Safety Protection of Computer Information Systems (Decree of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China (No. 147)
- Administrative Measures for the Multi-level Protection of Information Security (GongTongZi[2007] No. 43)
1.2.Standards
- The GB/T 22239-2019 Basic Requirements for the Multi-level Protection of Information Security Technology
- The GB/T 25070-2019 Information Security Technology Cybersecurity Multi-level Protection Security Design Technical Requirements
- The GB/T 28448-2019 Information Security Technology Cybersecurity Multi-level Protection Assessment Requirements
- The GB/T 25058-2019 Information Security Technology-Implementation Guide for Cybersecurity Classified Protection
1.3.Objects: Network Operators
The grading objects in this Specification refer to local government departments,enterprises and institutions or representative and other social organizations, who build, operate, and use basic information networks, cloud computing platforms/systems, big data applications/platforms/resources, Internet of Things, industrial control systems and systems using mobile internet technology, data resources and information systems that host independent business applications.
Network operators shall, according to therequirements of the multi-level protection system, fulfill their security obligations to ensure that the network is free from interference, damage, or unauthorized access, and prevent network data from being divulged, stolen, or falsified.
2.Assessment Procedure
2.1.General Procedure Flow
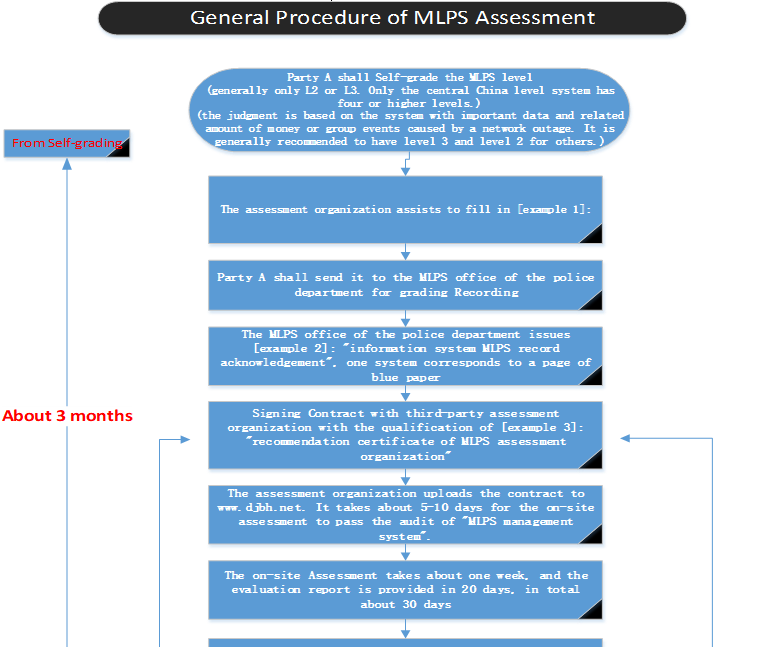
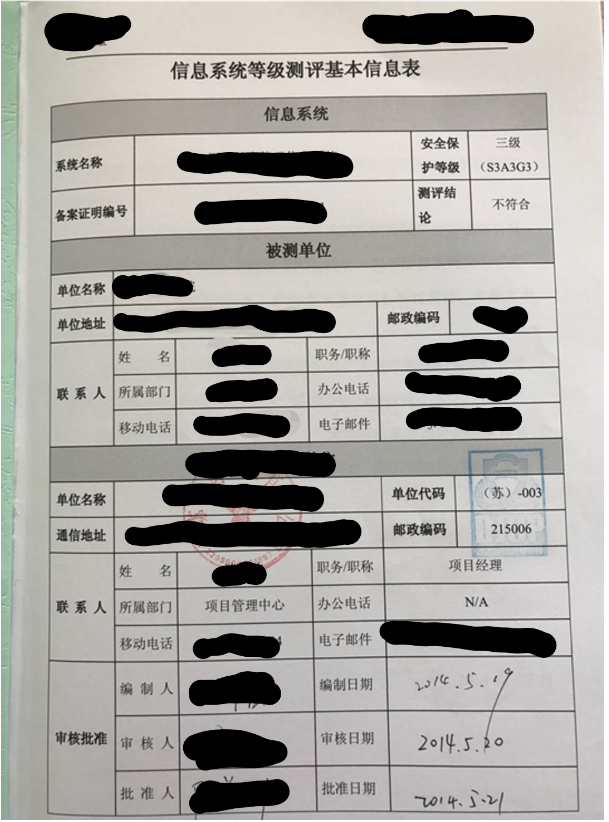
2.1.1.Examples 1《MLPS record form》, provided by assessment organization.

2.1.2.Examples 2《MLPS record certificate》, issued by the police department.

2.1.3.Examples 3《Recommendation certificate of MLPS assessment organization》

2.1.4.Examples 4《Assessment report》
2.2.Self-Grading
The network operator shall fill the application form (template form sees Annex 1, because only the Chinese form will be accepted, therefore we have not translated it) according to its own network/system situation.
Which level to take is based on the below matrix:
| Harmed objects when the network/system is damaged | Severity of the harm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| harm | serious harm | particularly serious damage | |
| legitimate rights and interests of the Chinese citizens | L1 | L2 | L3 |
| social order and the public interest | L2 | L3 | L4 |
| National Security | L3 | L4 | L5 |
When the network topology, usage, service scope/objects or handled data change, the corresponding security Level should also be re-graded.
Normally for manufacture companies based on our experience, maximum L2 is sufficient. Even L1 is also acceptable.
Due to the new situation in 2021, all the acknowledgement of self-grading above level 2 to WFOE in our region is currently not successful. Which means WFOE can prepare themselves for the MLPS without getting official assessment.
2.3.Onsite Assessment
The Assessment Organization shall hand the application form to the MLPS of the city (sees Annex 2), the MLPS office of the city invites three or more singular experts to conduct the review and notifies the district network security police to participate in the assessment meeting.
Before the start of the assessment, the experts participating in the assessment shall select an expert as the leader of the assessment work, the group leader hosts the review meeting.
The responsible person of the applicant the basics of the network and information systems reports specifics of the network and information system shall be to the review team on, including but not limited to:
1.the responsibility of the subject:
(1)planning and design, project approval, development and construction, running time of the Information system;
(2)Project supervisor, development unit, system integration and security integrator, supplier of network equipment and security products, security service providers (including operations and maintenance) and so on;
(3)The location server room of the system, the responsible department and the user department, etc.
2.the application of system functions:
(1)The programming language and database management software used by the system, as well as the version;
(2)This number, brand, model and quantity of application servers, database types and the number of database servers set up by the system;
(3)the main functions of the system;
(4)whether the system provides online services;
(5)whether there is mobile app;
(6)whether the system has adopted big data, cloud computing, etc.
(7)User type and quantity.
If the system cannot be demonstrated onsite, screenshot should be taken for each function page and make it to a presentation file.
3.network structure of the system:
(1)The network architecture of the system;
(2)The number of outbound connections and bandwidth;
(3)core network equipment deployed at the network boundary;
(4)the situation of safety protection products (indicating the brand, model);
(5)policy and state of security equipment;
(6)A brief introduction to network architecture, zone and boundary definition and security approaches, etc.
4.data situation:
(1)The size and type of data collected by the system (including personal information of citizens) and the collection, storage, transmission, use, provision, destruction and other aspects of security protection approaches;
(2)Whether
a data interface is provided to a third party, if any, describe it clearly; And whether non-disclosure agreements are signed;
(3)Which fields are collected from the core data and how much is the total amount;
(4)Which fields (including mobile phone numbers and identity cards) are collected as citizens’ personal information and the total amount of them.
(5)A brief overview of the main data types, quantities, and how to store them.
5.the self-grading situation and reasons:
Introduce the security level of the applicant’s system and explain the relevant level of the proposed level. If there is superior guidance, please bring together the expert group.
6.Expert assessment:
According to the reporting situation of the applicant, the assessment experts based on questioning and accessing to documents, etc. review the proposed level of applied information system.
Assessed contents include, but are not limited to, the following:
(1)Review the subject of responsibility: through questioning, access to documents and other forms, check whether the applicant has a responsibility to the security supervisor for the graded information system.
(2)Review rating objects: through questioning, access to materials and on-site viewing to examine whether the grading object has three basic elements of the information system: Clear responsibility entities; relatively independent businessapplications; multiple interconnected resources. Avoid putting a single system component (e.g. server, terminal, network devices, etc.), as a grading object;
(3)Review the object and the impact of the damage from the object: through the material provided by the network operator to explain clear network and information system objects and the reasons for the impact of the damage from the object in expert opinions.
7.Assessment result:
After the on-site assessment is completed, the experts of the group leader shall jointly determine the rationality of the applicant’s grading object, with all signatures of experts (avoiding applicant of the grading object onsite).
During the assessment, if significant safety risks were found to the grading object, recommendations should be made at the end of the assessment opinion, so as to facilitate the timely rectification of the network operator.
3.Assessment Items
3.1.Level 2
Security Category Security sub-category Number of assessment items Comments
Physical security Selection of physical location 1 Evaluate whether the physical server room is in the building with the ability of shockproof, windproof and rainproof
Physical access control 2 The examination and approval control means of entering and leaving the server room and the entrance and exit of the server room need to be attended by special personnel
Theft and vandalism 5 Evaluate the security of equipment and communication cables in the server room and the anti-theft alarm facilities.
Lightning protection 2 Evaluate the construction of building lightning protection and induction lightning protection and AC power ground wire
Fire prevention 1 Evaluate the setting of automatic monitoring fire protection system and the fire-fighting equipment.
Waterproof and damp proof 3 Evaluate the water pipe setting, rainwater infiltration, condensation and underground water transfer and infiltration in the server room.
Antistatic 1 Evaluate the anti-corrosion measures of key equipment.
Temperature and humidity control 1 Evaluate the temperature and humidity control measures of the server room.
Power supply 2 Evaluate the power supply line voltage stabilization, overvoltage and standby power supply in the server room.
Electromagnetic protection 1 Evaluate the isolation of power line and communication cable
Total 19
Network security Structural safety 4 Main verification: the processing capacity of key network equipment, whether the network bandwidth meets the business requirements, whether the network topology is consistent, and whether the subnet is divided.
Access control 4 Main verification: border network device access control function, system and dial-up access restrictions.
Security audit 2 Main verification: network equipment log collection, and audit records detailed records.
Boundary integrity check 1 Main verification: whether it can check the behavior of unauthorized devices connecting to the internal network.
Intrusion Prevention 1 Main verification: deployment and usage of IDS.
Network equipment protection 6 Main verification: user identification, administrator login address restriction, user identity uniqueness, password policy, login policy, remote management policy.
Total 18
Host security Identification 5 Main verification: user identification method, account and user correspondence, account and password length setting, password change cycle, etc; Login failure handling function settings.
Access control 4 Main verification: privilege separation of privileged users; Access right of default account; Processing of redundant and overdue accounts.
Security audit 4 Main verification: coverage of safety audit; Record content integrity; Prevent audit records from being deleted and covered.
Intrusion Prevention 1 Main verification: operating system component installation and patch upgrade.
Malicious code prevention 2 Main verification: use and upgrade of anti-virus and malicious code products. Support the unified management of anti malware software.
Resource control 3 Main verification: terminal login restriction mode and security policy
Total 19
Application Security Identification 4 Main verification: identity identification and authentication, authentication information complexity, login failure processing function and user identity uniqueness check, etc.
Access control 4 Main verification: independent access control function, minimum required authority and mutual restriction.
Security audit 3 Main verification: coverage of safety audit; Record content integrity; Prevent audit records from being deleted and covered.
Communication integrity 1 Main verification: Communication cryptography technology ensures the integrity of data communication process.
Communication confidentiality 2 Main verification: whether to use cryptographic technology for session initialization verification and encryption of sensitive information in the communication process.
Software fault tolerance 2 Main verification: data validation; Whether the fault can provide some functions.
Resource control 3 Main verification: automatic end session function, maximum number of Concurrent Session connections limit, multiple concurrent sessions limit for a single account.
Total 19
Data security Data integrity 1 Main verification: identify the integrity of information and important business data in the transmission process.
Data confidentiality 1 Main verification: use encryption or other protection measures to identify the storage confidentiality of information.
Backup and recovery 2 Main verification: backup and recovery of important information; Hardware redundancy of network equipment.
Total 4
Safety management system Management system 3 Main verification: overall security strategy construction; Establish safety management system for important management contents in safety activities; Establishment of personnel management operation procedures.
Development and release 3 Main verification: the establishment of the responsible department for the formulation of the safety management system; Establishment, review and release of safety management system.
Review and revision 1 Main verification: review and revision of safety management system
Total 7
Post setting 2 Main verification: establishment of safety management posts and clarification of responsibilities.
Staffing 2 Main verification: staffing of safety management posts.
Authorization and approval 2 The main verification is to authorize the approval department and the approving person according to the responsibilities of each department and post; The approval process for key activities shall be established and signed by the approval person.
Communication and cooperation 2 Main verification: communication and cooperation among management personnel, internal organizations and information functional departments; Cooperation and communication among brother units, public security organs and telecommunication companies.
Audit and inspection 1 Main verification: standardization and implementation of system safety inspection.
Safety management organization Total 9
Personnel safety management Personnel recruitment 3 Main verification: standardized management of personnel recruitment process; Sign the confidentiality agreement for the employed personnel.
Personnel leaving post 3 Main verification: control of personnel departure process;
Personnel assessment 1 Main verification: conduct safety skill and safety cognition assessment for each daring personnel.
Safety awareness education and training 3 Main verification: formulation and implementation of safety training plan.
Access management of external personnel 1 Main verification: approval and supervision of external personnel entering important areas. And grade record.
Total 11
System construction management System grading 3 Main verification: whether the security protection level of the information system is clear, and the method and reason for determining the security protection level in written form, to ensure that the grading results are approved by relevant departments.
Security scheme design 4 Main verification: the overall planning and design of the information security work of the system.
Purchase and use of products 3 Main verification: purchase and use management measures of information security products in the system.
Self developed software 3 Main verification: management of self-development of software within the system
Outsourcing software development 4 Main verification: the quality of outsourcing software to ensure the safety and availability of outsourcing software.
Project implementation 2 Main verification: implementation of information system engineering.
Test acceptance 3 Main verification: acceptance of information system engineering.
System delivery 3 Main verification: delivery of information system engineering.
Security service provider selection 3 Main verification: selection of relevant security service providers and service management measures in the system.
Total 28
System operation and maintenance management Environmental management 4 Main verification: daily management of server room infrastructure and office environment.
Asset management 2 Main verification: asset list preservation measures; Establish asset safety management system.
Media management 4 Main verification: storage, filing, destruction and classified management measures of various media.
Device management 4 Main verification: management of daily use, operation and maintenance of all kinds of equipment.
Network security management 6 Main verification: Construction of safety management system and inspection of illegal networking.
System security management 6 Main verification: system access control, patch, daily vulnerability scanning and audit management.
Malicious code prevention management 3 Main verification: the management of malicious code detection, analysis and other preventive work.
Password management 1 Main verification: the institutionalization and implementation of password use.
Change management 2 Main verification: the institutionalization of change activities and the standardized management before, during and after the change.
Backup and recovery management 3 Main verification: daily backup management of system data and system recovery management.
Security incident handling 4 Main verification: the construction of security incident reporting and disposal system and the standardized management of different security incident handling processes.
Emergency plan management 2 Main verification: formulate emergency plans for different events and train system idlers on emergency plans.
Total 41
Total 66 items 175 indexes
3.2.Level 3
| Security Category | Security sub-category | Number of assessment items | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical security | Selection of physical location | 2 | Evaluate whether the physical server room is in a building with the ability of shockproof, windproof and rainproof |
| Physical access control | 4 | The examination and approval control means of entering and leaving the server room and the entrance and exit of the server room need to be attended by special personnel | |
| Theft and vandalism | 6 | Evaluate the security of equipment and communication cables in the server room and the anti-theft alarm facilities | |
| Lightning protection | 3 | Evaluate the construction of building lightning protection and induction lightning protection and AC power ground wire | |
| Fire prevention | 3 | Evaluate the setting of automatic monitoring fire protection system and the fire-fighting equipment | |
| Waterproof and damp proof | 4 | Evaluate the water pipe setting, rainwater infiltration, condensation and underground water transfer and infiltration in the server room | |
| Antistatic | 2 | Evaluate the anti-static measures of main equipment | |
| Temperature and humidity control | 1 | Temperature and humidity control measures of assessment room | |
| Power supply | 4 | Evaluate the power supply line voltage stabilization, overvoltage and standby power supply in the server room | |
| Electromagnetic protection | 3 | Assessment of electromagnetic interference and electromagnetic protection | |
| Total | 32 | ||
| Network security | Structural safety | 7 | Main verification: processing capacity of main network equipment, whether network bandwidth meets business requirements, whether network topology is consistent, subnet division and isolation, bandwidth priority allocation of important services |
| Access control | 8 | Main verification: border network equipment access control function, system and dial-up access restrictions, information content filtering in and out of the network, maximum network traffic and connections, and measures to prevent address deception | |
| Security audit | 4 | Main verification: network equipment log collection, detailed records of audit records, audit report generation and protection measures for audit records | |
| Boundary integrity check | 2 | Main verification: whether the unauthorized equipment can be connected to the internal network independently to check, locate and block; Check, locate and block the behavior of internal users’ private external connection | |
| Intrusion Prevention | 2 | Main verification: deployment and usage of IDS | |
| Malicious code prevention | 2 | Main detection: detection and removal of malicious code at the network boundary | |
| Network equipment protection | 8 | Main verification: user identification, administrator login address restriction, user identity uniqueness, password policy, login policy, remote management policy and user authority separation | |
| Total | 33 | ||
| Host security | Identification | 6 | Main verification: user authentication method, account and user correspondence, account and password length settings, password change cycle, etc; Login failure handling function settings |
| Access control | 7 | Main verification: privilege separation of privileged users; Access right of default account; Disposal of surplus and overdue accounts | |
| Security audit | 6 | Main verification: coverage of safety audit; Record content integrity; Prevent audit records from being deleted and covered | |
| Residual information protection | 2 | Main inspection: the clearance of user identification information, system files, directories and data in the storage space | |
| Intrusion Prevention | 3 | Main verification: operating system component installation and patch upgrade, intrusion behavior record and alarm, and recovery measures after damage | |
| Malicious code prevention | 3 | Main verification: usage and upgrade of anti-virus and malicious code products, unified management of anti malicious code software, and malicious code library different from network anti malicious code products | |
| Resource control | 5 | Main verification: terminal login restriction mode and security policy, monitoring server resource usage and minimum alarm measures | |
| Total | 32 | ||
| Application Security | Identification | 5 | Main verification: identity identification and authentication, complexity of user name and password, whether to use two or more combination of authentication technologies, login failure processing function and uniqueness check of user identity |
| Access control | 6 | Main verification: the function of independent access control, the minimum required authority and the relationship of mutual restriction, the function of setting sensitive marks on important information resources and controlling the operation of important information resources with sensitive marks | |
| Security audit | 4 | Main verification: coverage of safety audit; Record content integrity; Prevent audit records from being deleted and covered; Functions of security audit statistics, query, analysis and audit report generation | |
| Residual information protection | 2 | Main inspection: the clearance of user identification information, system files, directories and data in the storage space | |
| Communication integrity | 1 | Main verification: Communication cryptography technology ensures the integrity of data communication process | |
| Communication confidentiality | 2 | Main verification: whether to use cryptographic technology for session initialization verification and encrypt the whole message or session process in the communication process | |
| Non-Repudiation | 2 | Main inspection: the function of providing primary evidence and receiving evidence of data | |
| Software fault tolerance | 2 | Main verification: data validation; Whether it can provide partial function and automatic protection function in case of failure | |
| Resource control | 7 | Main verification: automatic end session function, maximum concurrent session connection number limit, multiple concurrent session limit of a single account, maximum and minimum resource allocation of a single account, alarm function of reaching the minimum value, service priority setting function | |
| Total | 31 | ||
| Data security | Data integrity | 2 | Main verification: integrity of user account information and important business data in the transmission process |
| Data confidentiality | 2 | Main verification: use encryption or other protection measures to ensure the storage confidentiality of user account information and important business data | |
| Backup and recovery | 4 | Main verification: backup and recovery of important information; Hardware redundancy of network equipment | |
| Total | 8 | ||
| Safety management system | Management system | 4 | Main verification: overall security strategy construction; Establish safety management system for important management contents in safety activities; Personnel management operating procedures establish and form a comprehensive information security management system composed of security strategy, management system and operating procedures |
| Development and release | 5 | Main verification: the establishment of the responsible department for the formulation of the safety management system; The formulation, audit and release of safety management system, whether there is a unified format and version control | |
| Review and revision | 2 | Main verification: review and revision of safety management system and safety management system | |
| Total | 11 | ||
| Safety management organization | Post setting | 4 | Main verification: safety management department, post establishment and clear responsibilities |
| Staffing | 3 | Main verification: staffing of safety management posts | |
| Authorization and approval | 4 | The main verification is to authorize the approval department and the approving person according to the responsibilities of each department and post; The approval process for important activities shall be established and signed by the examiner | |
| Communication and cooperation | 5 | Main verification: communication and cooperation among management personnel, internal organizations and information functional departments; Cooperation and communication among brother units, public security organs and telecommunication companies; Establish contact list of external units and employ information security experts as perennial security consultants | |
| Audit and inspection | 4 | Main verification: standardization and implementation of system safety inspection, regular and comprehensive inspection | |
| Total | 20 | ||
| Personnel safety management | Personnel recruitment | 4 | Main verification: standardized management of personnel recruitment process; Signing confidentiality agreement for employed personnel; Key post personnel sign post safety agreement |
| Personnel leaving post | 3 | Main verification: personnel departure process control | |
| Personnel assessment | 3 | Main verification: carry out safety inspection, strict safety review and skill assessment for all post personnel, and keep assessment results and records | |
| Safety awareness education and training | 4 | Main verification: formulation and implementation of safety training plan | |
| External personnel access management | 2 | Main verification: approval and supervision of external personnel entering important areas, and filing at different levels | |
| Total | 16 | ||
| System construction management | System grading | 4 | Main verification: whether the information system defines its security protection level and the method and reason for determining the security protection level in written form, ensures that the grading results are approved by relevant departments, and whether experts are organized to demonstrate and approve |
| Security scheme design | 5 | Main verification: the overall planning and design of the system’s information security work | |
| Purchase and use of products | 4 | Main verification: purchase and use management measures of information security products in the system | |
| Self developed software | 5 | Main verification: management of self software development in the system | |
| Outsourcing software development | 4 | Main verification: the quality of outsourcing software, to ensure the safety and availability of outsourcing software | |
| Project implementation | 3 | Main verification: implementation of information system engineering | |
| Test acceptance | 5 | Main verification: acceptance of information system engineering | |
| System delivery | 5 | Main verification: delivery of information system engineering | |
| System record | 3 | Main verification: record of information system | |
| Grade assessment | 4 | Main verification: assessment and rectification of information system | |
| Security service provider selection | 3 | Main verification: selection of relevant security service providers and service management measures in the system | |
| Total | 45 | ||
| System operation and maintenance management | Environmental management | 4 | Main verification: daily management of server room infrastructure and office environment |
| Asset management | 4 | Main verification: asset list preservation measures; Establish asset safety management system, classify and mark assets | |
| Media management | 6 | Main verification: establish media security management system, take measures for storage, filing, destruction and classification management of various media, and take encryption measures for data and software in important media | |
| Device management | 5 | Main verification: establish equipment maintenance management system to manage the daily use, operation and maintenance of all kinds of equipment | |
| Monitoring management and safety management center | 3 | Main inspection: take monitoring and management measures to monitor and alarm the communication line, host, network equipment and application software; Establish a security management center to centrally manage equipment status, malicious code, patch upgrade, security audit and other security related matters | |
| Network security management | 8 | Main verification: Construction of safety management system and inspection of illegal networking | |
| System security management | 7 | Main verification: system access control, patches, daily vulnerability scanning and audit management | |
| Prevention and management of malicious code | 4 | Main verification: the management of malicious code detection, analysis and other preventive work | |
| Password management | 1 | Main verification: the institutionalization and implementation of password use | |
| Change management | 4 | Main verification: institutionalized construction of change activities and standardized management before, during and after change | |
| Backup and recovery management | 5 | Main verification: daily backup management of system data and system recovery management | |
| Security incident handling | 6 | Main verification: the construction of security incident reporting and handling system and the standardized management of different security incident handling processes | |
| Emergency plan management | 5 | Main verification: formulate emergency plans for different events, train relevant personnel of the system, and conduct regular drills, etc | |
| Total | 62 | ||
| Total | 73 items | 290 indexes |
3.3.MLPS high-risk items & rectification Approaches
| NO. | Security Category | Security Sub-Category | Level-2 rectification | Level-3 rectification | Investment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Physical security | 1 | Selection of physical location | |||
| 2 | 2 | Physical access control | Electronic access control | Medium | ||
| 3 | 3 | Theft and vandalism | Video monitoring system / burglar alarm system | Video monitoring system / burglar alarm system | Medium | |
| 4 | 4 | Lightning protection | lightning protector | Low | ||
| 5 | 5 | Fire prevention | Fire-fighting equipment and automatic fire alarm system | Automatic fire-fighting system | High | |
| 6 | 6 | Waterproof and damp proof | Dehumidifier | Waterproof detection and alarm | Medium high | |
| 7 | 7 | Antistatic | Anti-static floor | Medium | ||
| 8 | 8 | Temperature and humidity control | Precision air conditioner | Precision air conditioner | High | |
| 9 | 9 | power supply | Voltage regulator, overvoltage protection equipment, UPS | Voltage regulator, overvoltage protection equipment, UPS, standby power supply system | High | |
| 10 | 10 | Electromagnetic protection | Electromagnetic shielding and electromagnetic interference device | Low | ||
| 11 | Network security | 1 | Structural safety | Core equipment redundancy | Medium | |
| 12 | 2 | Access control | Border firewall | Border firewall | Medium high | |
| 13 | 3 | Security audit | Log audit system | Log audit system | Medium | |
| 14 | 4 | Boundary integrity check | Private external connection control (terminal security management system) | Network access control / private external connection control (terminal security management system) | Medium | |
| 15 | 5 | Intrusion Prevention | Intrusion detection / defense system | Intrusion prevention system | Medium | |
| 16 | 6 | Malicious code prevention | Network anti virus gateway | Medium | ||
| 17 | 7 | Network equipment protection | Network operation and maintenance management system (Jumper machine) | Medium | ||
| 18 | Host security | 1 | Identification | Multi factor identity authentication system | Medium | |
| 19 | 2 | Access control | Host security environment system | Medium | ||
| 20 | 3 | Security audit | Log audit system | Log audit system | Medium | |
| Database audit system | Database audit system | |||||
| 21 | 4 | Residual information protection | Host security environment system | Medium | ||
| 22 | 5 | Intrusion Prevention | Patch management system (free WSUS or terminal management system with patch management module) | Host intrusion prevention software / patch management system (free WSUS or terminal management system patch management module) | Medium | |
| 23 | 6 | Malicious code prevention | Network version antivirus software | Network version anti-virus software (host anti malicious code products should have different malicious code libraries from network anti malicious code products) | Medium | |
| 24 | 7 | Resource control | Security monitoring center host system resource monitoring module | |||
| 25 | Application Security | 1 | Identification | Multi factor identity authentication system | Medium | |
| 26 | 2 | Access control | ||||
| 27 | 3 | security audit | Application system audit module configuration | Log integrated audit system application audit module / application system audit module configuration | Medium | |
| 28 | 4 | Residual information protection | ||||
| 29 | 5 | Communication integrity | ||||
| 30 | 6 | Communication confidentiality | ||||
| 31 | 7 | Non-Repudiation | Digital certificate | |||
| 32 | 8 | Software fault tolerance | Web Application Firewall | Web application firewall / webpage tamper proof system | Medium | |
| 33 | 9 | Resource control | Security monitoring center application system resource monitoring module | Medium | ||
| 34 | Data security and backup | 1 | Data integrity | Data transmission integrity protection / data storage integrity protection (data security protection system) | Medium | |
| 35 | 2 | Data confidentiality | Data transmission encryption / data storage encryption (data security protection system) | Medium | ||
| 36 | 3 | Backup and recovery | Local data backup and recovery system (full backup once a day), communication line and hardware redundancy, remote data backup and network structure redundancy | High | ||
| 37 | System operation and maintenance management | 1 | Monitoring management and safety management center | Environmental monitoring system (such as power distribution, UPS, air conditioning, temperature and humidity, water leakage, smoke, video, access control, fire protection system, etc.) | Medium | |
| 38 | 2 | Safety monitoring center (such as: monitoring and alarming of communication line, host, network equipment and application software, network traffic, user behavior, etc.) | Medium | |||
| 39 | 3 | Security Management Center (such as centralized management of equipment status, malicious code, patch upgrade, security audit and other security related matters) | Medium | |||
| Summary | There are 66 assessment items and 175 assessment indexes | There are 73 assessment items and 290 assessment indexes | ||||
4.Conclusion
Based on our experience, the most SME manufactures, who don’t have any web service will process/collect the civilian information or serve the public, have no problem passing MLPS assessment for level 2. Most of them have internal system like MES/ERP dedicating for internal usage with strong authentication and security methods already. If all the high-risk items are covered, then passing it will not be a problem with a proper report. And level 3 is unnecessary for SME manufactures to apply, it costs just the assessment cost and bring less back.
For the network/host items which would fail the assessment like: firewall/anti-virus are widely deployed in modern IT environment, especially for WFOEs. IDS/IPS functions are normally integrated in the firewall system; Log auditor can be acknowledged by any syslog server. Since the brand/model is currently not whitelisted/blacklisted. Any similar device fulfills the function counts.
For physical aspect, SMEs which don’t have a good server room environment, cloud-based environment like Microsoft Azure 21Vnet, China-Telecom ecloud/iDC is already MLPS certificated. If there is a managed environment monitor system to monitor the UPS battery, temperature and humidity, it would be helpful.
For the management aspect, a disaster-recovery plan already written would be most helpful, not only for passing MLPS, but also for the business continuity of its own.
5.Annex
1.Annex1_SelfGrading_网络安全等级保护定级报告
2.Annex2_MLPS_RecordForm网络安全等级保护备案表